Burma
Background Information
SOS Children volunteers helped choose articles and made other curriculum material All children available for child sponsorship from SOS Children are looked after in a family home by the charity. Read more...
| Republic of the Union of Myanmar ပြည်ထောင်စု သမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: Kaba Ma Kyei Till the End of the World |
||||||
|
Location of Burma (green)
in ASEAN (dark grey) — [Legend] |
||||||
| Capital | Naypyidawa 19°45′N 96°6′E |
|||||
| Largest city | Yangon (Rangoon) | |||||
| Official languages | Burmese | |||||
| Recognised regional languages |
|
|||||
| Official scripts | Burmese script | |||||
| Ethnic groups |
|
|||||
| Demonym | Burmese / Myanma | |||||
| Government | Unitary presidential constitutional republic | |||||
| - | President | Thein Sein | ||||
| - | Vice Presidents |
|
||||
| Legislature | Assembly of the Union | |||||
| - | Upper house | House of Nationalities | ||||
| - | Lower house | House of Representatives | ||||
| Formation | ||||||
| - | Pagan Dynasty | 23 December 849 | ||||
| - | Toungoo Dynasty | 16 October 1510 | ||||
| - | Konbaung Dynasty | 29 February 1752 | ||||
| - | Independence (from United Kingdom) |
4 January 1948 | ||||
| - | Coup d'état | 2 March 1962 | ||||
| - | New constitution | 30 March 2011 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 676,578 km2 ( 40th) 261,227 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 3.06 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2010 estimate | 60,280,000 ( 24th[2]) | ||||
| - | 1983 census | 33,234,000 | ||||
| - | Density | 73.9/km2 ( 119th) 191.5/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2012 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $88.751 billion | ||||
| - | Per capita | $1,393 | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2012 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $54.416 billion | ||||
| - | Per capita | $854 | ||||
| HDI (2012) | low · 149th |
|||||
| Currency | Kyat (K) ( MMK) |
|||||
| Time zone | MST ( UTC+06:30) | |||||
| Drives on the | rightb | |||||
| Calling code | +95 | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | MM | |||||
| Internet TLD | .mm | |||||
| a. | Some governments recognise Yangon (Rangoon) as the national capital. | |||||
| b. | Road infrastructure is still for driving on the left. | |||||
Burma ( / ˈ b ɜr m ə / BUR-mə), a historic name for the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, also known simply by another historic name, Myanmar, ( / ˈ m j ɑː n ˌ m ɑr / MYAHN-mar, / ˈ m aɪ æ n m ɑr / or / ˈ m j æ n m ɑr /), is a sovereign state in Southeast Asia bordered by China, Thailand, India, Laos and Bangladesh. One-third of Burma's total perimeter of 1,930 kilometres (1,200 miles) forms an uninterrupted coastline along the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. Its population of over 60 million makes it the world's 24th most populous country and, at 676,578 km2 (261,227 sq mi), it is the world's 40th largest country and the second largest in Southeast Asia.
The country has been under military control since a coup d'état in 1962. During this time, the United Nations and several other organizations have reported consistent and systematic human rights violations in the country, including genocide, the use of child soldiers, systematic rape, child labour, slavery, human trafficking and a lack of freedom of speech. Since the military began relinquishing more of its control over the government, however – coupled with its release in 2011 of Burma's most prominent human rights activist, Aung San Suu Kyi – the country's foreign relationships have improved rapidly, especially with major powers such as the European Union, Japan, and the United States. Trade and other economic sanctions, for example, imposed by the European Union and the United States, have now been eased.
Burma is a country rich in precious stones, oil, natural gas and other mineral resources. In 2011, its GDP stood at US$82.7 billion and was estimated as growing at an annual rate of 5.5%.
In 2013, rights groups reported that Burmese authorities have begun ethnic cleansing the Rohingya minority in western Burma, resulting in hundreds of thousands of refugees fleeing across the border to Bangladesh and also to Thailand where they may be held in squalid conditions.
Etymology
In 1989, the military government officially changed the English translations of many names dating back to Burma's colonial period, including that of the country itself: "Burma" became "Myanmar". The renaming remains a contested issue. Many political and ethnic opposition groups and countries continue to use "Burma" because they do not recognise the legitimacy of the ruling military government or its authority to rename the country.
The country's official full name is the "Republic of the Union of Myanmar" / ˈ m j ɑː n ˌ m ɑr / ( Burmese: ပြည်ထောင်စု သမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်, Pyidaunzu Thanmăda Myăma Nainngandaw, pronounced: [pjìdàʊɴzṵ θàɴməda̰ mjəmà nàɪɴŋàɴdɔ̀]). Some countries, however, have not recognized this name and use the short form "Union of Burma" instead.
In English, the country is popularly known by either of its short names "Burma" or "Myanmar". Both these names are derived from the name of the majority Burmese Bamar ethnic group. Myanmar is considered to be the literary form of the name of the group, while Burma is derived from "Bamar", the colloquial form of the group's name. Depending on the register used, the pronunciation would be Bama (pronounced: [bəmà]) or Myamah (pronounced: [mjəmà]). The name Burma has been in use in English since the time of British colonial rule.
Burma continues to be used in English by the governments of many countries, including the United Kingdom and Canada. The United States uses both Myanmar and Burma. The United Nations uses Myanmar, as do the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, Russia, Germany, Norway, China, India, Australia and Japan.
There are variations of "Myanmar" when translated to local languages. In Spain and Italy, "Myanmar" is commonly known as "Birmania". The Government of Brazil uses "Mianmar".
History
Burma is home to some of the early civilizations of Southeast Asia including the Pyu and the Mon. In the 9th century, the Burmans of the Kingdom of Nanzhao entered the upper Irrawaddy valley and, following the establishment of the Pagan Empire in the 1050s, the Burmese language and culture slowly became dominant in the country. During this period, Theravada Buddhism gradually became the predominant religion of the country. The Pagan Empire fell due to the Mongol invasions (1277–1301), and several warring states emerged. In the second half of the 16th century, reunified by the Taungoo Dynasty, the country was for a brief period the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia. The early 19th century Konbaung Dynasty ruled over an area that included modern Burma as well as Manipur and Assam. Since independence in 1948, the country has been in one of the longest running civil wars among the country's myriad ethnic groups that remains unresolved. From 1962 to 2011, the country was under military rule. The military junta was officially dissolved in 2011 following a general election in 2010 and a nominally civilian government installed, though the military retains enormous influence.
Prehistory
Archaeological evidence shows that Homo erectus lived in the region now known as Burma as early as 750,000 years ago and Homo sapiens about 11,000 BC, in a Stone Age culture called the Anyathian, when plants and animals were first domesticated and polished stone tools appeared in Burma. The Bronze Age arrived circa 1500 BC when people in the region were turning copper into bronze, growing rice and domesticating poultry and pigs; they were among the first people in the world to do so. The Iron Age arrived around 500 BC when iron-working settlements had emerged in an area south of present-day Mandalay. Evidence also shows rice-growing settlements of large villages and small towns that traded with their surroundings as far as China between 500 BC and 200 AD.
Around the 2nd century BC the first-known city-states emerged in central Burma. The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu, the earliest inhabitants of Burma of whom records are extant, from present-day Yunnan. The Pyu culture was heavily influenced by trade with India, importing Buddhism as well as other cultural, architectural and political concepts, which would have an enduring influence on later Burmese culture and political organization. By the 9th century AD several city-states had sprouted across the land: the Pyu states in the central dry zone, Mon states along the southern coastline and Arakanese states along the western littoral. The balance was upset when the Pyu states came under repeated attacks from the Kingdom of Nanzhao between the 750s and the 830s. In the mid-to-late 9th century the Mranma (Burmans/Bamar) of Nanzhao founded a small settlement at Pagan (Bagan). It was one of several competing city-states until the late 10th century when it grew in authority and grandeur.
Imperial Burma
Pagan gradually grew to absorb its surrounding states until the 1050s–1060s when Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, the first ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Pagan Empire and the Khmer Empire were two main powers in mainland Southeast Asia. The Burmese language and culture gradually became dominant in the upper Irrawaddy valley, eclipsing the Pyu, Mon and Pali norms by the late 12th century. Theravada Buddhism slowly began to spread to the village level although Tantric, Mahayana, Brahmanic, and animist practices remained heavily entrenched. Pagan's rulers and wealthy built over 10,000 Buddhist temples in the Pagan capital zone alone. Repeated Mongol invasions (1277–1301) toppled the four-century-old kingdom in 1287.
Pagan's collapse was followed by 250 years of political fragmentation that lasted well into the 16th century. Like the Burmans four centuries earlier, Shan migrants who arrived with the Mongol invasions stayed behind. Several competing Shan states came to dominate the entire northwestern to eastern arc surrounding the Irrawaddy valley. The valley too was beset with petty states until the late 14th century when two sizable powers, Ava Kingdom and Hanthawaddy Kingdom, emerged. In the west, a politically fragmented Arakan was under competing influences of its stronger neighbors until the Kingdom of Mrauk U unified the Arakan coastline for the first time in 1437.
Early on, Ava fought wars of unification (1385–1424) but could never quite reassemble the lost empire. Having held off Ava, Hanthawaddy entered its golden age, and Arakan went on to become a power in its own right for the next 350 years. In contrast, constant warfare left Ava greatly weakened, and it slowly disintegrated from 1481 onward. In 1527, the Confederation of Shan States conquered Ava itself, and ruled Upper Burma until 1555.
Like the Pagan Empire, Ava, Hanthawaddy and the Shan states were all multi-ethnic polities. Despite the wars, cultural synchronization continued. This period is considered a golden age for Burmese culture. Burmese literature "grew more confident, popular, and stylistically diverse", and the second generation of Burmese law codes as well as the earliest pan-Burma chronicles emerged. Hanthawaddy monarchs introduced religious reforms that later spread to the rest of the country. Many splendid temples of Mrauk U were built during this period.
Political unification returned in the mid-16th century, due to the efforts of one tiny Toungoo (Taungoo), a former vassal state of Ava. Toungoo's young, ambitious king Tabinshwehti defeated the more powerful Hanthawaddy in 1541. His successor Bayinnaung went on to conquer a vast swath of mainland Southeast Asia including the Shan states, Lan Na, Manipur, the Chinese Shan states, Siam, Lan Xang and southern Arakan. However, the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia unravelled soon after Bayinnaung's death in 1581, completely collapsing by 1599. Siam seized Tenasserim and Lan Na, and Portuguese mercenaries established Portuguese rule at Syriam (Thanlyin).
The dynasty regrouped and defeated the Portuguese in 1613 and Siam in 1614. It restored a smaller, more manageable kingdom, encompassing Lower Burma, Upper Burma, Shan states, Lan Na and upper Tenasserim. The Restored Toungoo kings created a legal and political framework whose basic features would continue well into the 19th century. The crown completely replaced the hereditary chieftainships with appointed governorships in the entire Irrawaddy valley, and greatly reduced the hereditary rights of Shan chiefs. Its trade and secular administrative reforms built a prosperous economy for more than 80 years. From the 1720s onward, the kingdom was beset with repeated Manipuri raids into Upper Burma, and a nagging rebellion in Lan Na. In 1740, the Mon of Lower Burma founded the Restored Hanthawaddy Kingdom. Hanthawaddy forces sacked Ava in 1752, ending the 266-year-old Toungoo Dynasty.
After the fall of Ava, one resistance group, Alaungpaya's Konbaung Dynasty defeated Restored Hanthawaddy, and by 1759, had reunited all of Burma (and Manipur), and driven out the French and the British who had provided arms to Hanthawaddy. By 1770, Alaungpaya's heirs had subdued much of Laos (1765), defeated Siam (1767), and defeated four invasions by China (1765–1769). With Burma preoccupied by the Chinese threat, Siam recovered its territories by 1770, and went on to capture Lan Na by 1776. Burma and Siam went to war until 1855, but all resulted in a stalemate, exchanging Tenasserim (to Burma) and Lan Na (to Siam). Faced with a powerful China and a resurgent Siam in the east, King Bodawpaya turned west, acquiring Arakan (1785), Manipur (1814) and Assam (1817). It was the second largest empire in Burmese history but also one with a long ill-defined border with British India.
The breadth of this empire was short lived. Burma lost Arakan, Manipur, Assam and Tenasserim to the British in the First Anglo-Burmese War (1824–1826). In 1852, the British easily seized Lower Burma in the Second Anglo-Burmese War. King Mindon tried to modernize the kingdom, and in 1875 narrowly avoided annexation by ceding the Karenni States. The British, alarmed by the consolidation of French Indo-China, annexed the remainder of the country in the Third Anglo-Burmese War in 1885.
Konbaung kings extended Restored Toungoo's administrative reforms, and achieved unprecedented levels of internal control and external expansion. For the first time in history, the Burmese language and culture came to predominate the entire Irrawaddy valley. The evolution and growth of Burmese literature and theatre continued, aided by an extremely high adult male literacy rate for the era (half of all males and 5% of females). Nonetheless, the extent and pace of reforms were uneven and ultimately proved insufficient to stem the advance of British colonialism.
British Burma
The country was colonized by Britain following three Anglo-Burmese Wars (1824–1885). British rule brought social, economic, cultural and administrative changes.
With the fall of Mandalay, all of Burma came under British rule, being annexed on 1 January 1886. Throughout the colonial era, many Indians arrived as soldiers, civil servants, construction workers and traders and, along with the Anglo-Burmese community, dominated commercial and civil life in Burma. Rangoon became the capital of British Burma and an important port between Calcutta and Singapore.
Burmese resentment was strong and was vented in violent riots that paralysed Yangon (Rangoon) on occasion all the way until the 1930s. Some of the discontent was caused by a disrespect for Burmese culture and traditions such as the British refusal to remove shoes when they entered pagodas. Buddhist monks became the vanguards of the independence movement. U Wisara, an activist monk, died in prison after a 166-day hunger strike to protest a rule that forbade him from wearing his Buddhist robes while imprisoned.
On 1 April 1937, Burma became a separately administered colony of Great Britain and Ba Maw the first Prime Minister and Premier of Burma. Ba Maw was an outspoken advocate for Burmese self-rule and he opposed the participation of Great Britain, and by extension Burma, in World War II. He resigned from the Legislative Assembly and was arrested for sedition. In 1940, before Japan formally entered the Second World War, Aung San formed the Burma Independence Army in Japan.
A major battleground, Burma was devastated during World War II. By March 1942, within months after they entered the war, Japanese troops had advanced on Rangoon and the British administration had collapsed. A Burmese Executive Administration headed by Ba Maw was established by the Japanese in August 1942. Wingate's British Chindits were formed into long-range penetration groups trained to operate deep behind Japanese lines. A similar American unit, Merrill's Marauders, followed the Chindits into the Burmese jungle in 1943. Beginning in late 1944, allied troops launched a series of offensives that led to the end of Japanese rule in July 1945. However, the battles were intense with much of Burma laid waste by the fighting. Overall, the Japanese lost some 150,000 men in Burma. Only 1,700 prisoners were taken.
Although many Burmese fought initially for the Japanese, some Burmese, mostly from the ethnic minorities, also served in the British Burma Army. The Burma National Army and the Arakan National Army fought with the Japanese from 1942 to 1944, but switched allegiance to the Allied side in 1945.
Following World War II, Aung San negotiated the Panglong Agreement with ethnic leaders that guaranteed the independence of Burma as a unified state. In 1947, Aung San became Deputy Chairman of the Executive Council of Burma, a transitional government. But in July 1947, political rivals assassinated Aung San and several cabinet members.
Independence
On 4 January 1948, the nation became an independent republic, named the Union of Burma, with Sao Shwe Thaik as its first President and U Nu as its first Prime Minister. Unlike most other former British colonies and overseas territories, it did not become a member of the Commonwealth. A bicameral parliament was formed, consisting of a Chamber of Deputies and a Chamber of Nationalities, and multi-party elections were held in 1951–1952, 1956 and 1960.
The geographical area Burma encompasses today can be traced to the Panglong Agreement, which combined Burma Proper, which consisted of Lower Burma and Upper Burma, and the Frontier Areas, which had been administered separately by the British.
In 1961, U Thant, then the Union of Burma's Permanent Representative to the United Nations and former Secretary to the Prime Minister, was elected Secretary-General of the United Nations, a position he held for ten years. Among the Burmese to work at the UN when he was Secretary-General was a young Aung San Suu Kyi, who went on to become winner of the 1991 Nobel Peace Prize.
Military rule
On 2 March 1962, the military led by General Ne Win took control of Burma through a coup d'état and the government has been under direct or indirect control by the military since then. Between 1962 and 1974, Burma was ruled by a revolutionary council headed by the general, and almost all aspects of society (business, media, production) were nationalized or brought under government control under the Burmese Way to Socialism, which combined Soviet-style nationalisation and central planning with the governmental implementation of superstitious beliefs. A new constitution of the Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma was adopted in 1974. Until 1988, the country was ruled as a one-party system, with the General and other military officers resigning and ruling through the Burma Socialist Programme Party (BSPP). During this period, Burma became one of the world's most impoverished countries.
There were sporadic protests against military rule during the Ne Win years and these were almost always violently suppressed. On 7 July 1962, the government broke up demonstrations at Rangoon University, killing 15 students. In 1974, the military violently suppressed anti-government protests at the funeral of U Thant. Student protests in 1975, 1976 and 1977 were quickly suppressed by overwhelming force.
In 1988, unrest over economic mismanagement and political oppression by the government led to widespread pro-democracy demonstrations throughout the country known as the 8888 Uprising. Security forces killed thousands of demonstrators, and General Saw Maung staged a coup d'état and formed the State Law and Order Restoration Council (SLORC). In 1989, SLORC declared martial law after widespread protests. The military government finalised plans for People's Assembly elections on 31 May 1989. SLORC changed the country's official English name from the "Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma" to the "Union of Myanmar" in 1989.
In May 1990, the government held free elections for the first time in almost 30 years and the National League for Democracy (NLD), the party of Aung San Suu Kyi, won 392 out of a total 489 seats (i.e., 80% of the seats). However, the military junta refused to cede power and continued to rule the nation as SLORC until 1997, and then as the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC) until its dissolution in March 2011.
On 23 June 1997, Burma was admitted into the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). On 27 March 2006, the military junta, which had moved the national capital from Yangon to a site near Pyinmana in November 2005, officially named the new capital Naypyidaw, meaning "city of the kings".
In August 2007, an increase in the price of diesel and petrol led to a series of anti-government protests that were dealt with harshly by the government. The protests then became a campaign of civil resistance (also called the Saffron Revolution.) led by Buddhist monks, hundreds of whom defied the house arrest of democracy advocate Aung San Suu Kyi to pay their respects at the gate of her house. The government finally cracked down on them on 26 September 2007. The crackdown was harsh, with reports of barricades at the Shwedagon Pagoda and monks killed. However, there were also rumours of disagreement within the Burmese armed forces, but none was confirmed. The military crackdown against unarmed Saffron Revolution protesters was widely condemned as part of the International reaction to the 2007 Burmese anti-government protests and led to an increase in economic sanctions against the Burmese Government.
In May 2008, Cyclone Nargis caused extensive damage in the densely populated, rice-farming delta of the Irrawaddy Division. It was the worst natural disaster in Burmese history with reports of an estimated 200,000 people dead or missing, and damage totaled to 10 billion dollars (USD), and as many as 1 million left homeless. In the critical days following this disaster, Burma's isolationist government hindered recovery efforts by delaying the entry of United Nations planes delivering medicine, food, and other supplies.
In early August 2009, a conflict known as the Kokang incident broke out in Shan State in northern Burma. For several weeks, junta troops fought against ethnic minorities including the Han Chinese, Va, and Kachin. During 8–12 August, the first days of the conflict, as many as 10,000 Burmese civilians fled to Yunnan province in neighbouring China.
Reforms and transition towards democracy
The goal of the Burmese constitutional referendum of 2008, held on 10 May 2008, is the creation of a "discipline-flourishing democracy". As part of the referendum process, the name of the country was changed from the "Union of Myanmar" to the "Republic of the Union of Myanmar" and general elections were held under the new constitution in 2010. Observer accounts of the 2010 election day describe the event as mostly peaceful; however, allegations were raised in regard to polling station irregularities, and the United Nations (UN) and a number of Western countries condemned the elections as fraudulent. One report documented 77 percent as the official turnout rate of the election. The military-backed Union Solidarity and Development Party later declared victory, stating that it had been favoured by 80 percent of the votes; however, the claim was disputed by numerous pro-democracy opposition groups with an assertion that the military regime engaged in rampant fraud to achieve such a result. The military junta was dissolved on 30 March 2011.
Since the 2010 election, the government has embarked on a series of reforms to direct the country towards liberal democracy, a mixed economy and reconciliation; although, the questioning of the motives that underpin such reforms has not ceased. The series of reforms includes the release of pro-democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi from house arrest, establishment of the National Human Rights Commission, granting of general amnesties for more than 200 political prisoners, new labour laws that permit labour unions and strikes, relaxation of press censorship, and the regulation of currency practices.
The impact of the post-election reforms has been observed in numerous areas, such as ASEAN's approval of Burma's bid for the position of ASEAN chair in 2014; the visit by United States Secretary of State Hillary Clinton in December 2011 for the encouragement of further progress—it was the first visit by a Secretary of State in more than fifty years (Clinton met with Burmese president Thein Sein, as well as opposition leader Daw Aung San Suu Kyi); and the participation of Aung San Suu Kyi's National League for Democracy (NLD) party in the 2012 by-elections, facilitated by the government's abolition of the laws that previously barred the NLD. As of April 2013, more than 200 political prisoners remain imprisoned, while conflict between the Burmese Army and local insurgent groups continues.
The by-elections occurred on 1 April 2012 and the NLD won 43 of the 45 available seats; previously an illegal organization, the NLD had never won a Burmese election up until this time. The 2012 by-elections was also the first time that international representatives were allowed to monitor the voting process in Burma. Following the announcement of the by-elections, the Freedom House organization raised concerns about "reports of fraud and harassment in the lead up to elections, including the March 23 deportation of Somsri Hananuntasuk, executive director of the Asian Network for Free Elections (ANFREL), a regional network of civil society organizations promoting democratization."
Civil war
Civil wars have been a constant feature of Burma's socio-political landscape since the attainment of independence in 1948. These wars are predominantly struggles for ethnic and sub-national autonomy, with the areas surrounding the ethnically Burman central districts of the country serving as the primary geographical setting of conflict. Foreign journalists and visitors require a special travel permit to visit the areas in which Burma's civil wars continue.
In October 2012 the number of ongoing conflicts in Burma included the Kachin conflict, between the Kachin Independence Army and the government; a civil war between the Rohingya Muslims, and the government and non-government groups in Arakan State; and a conflict between the Shan, Lahu and Karen minority groups, and the government in the eastern half of the country.
A widely publicised Burmese conflict was the 2012 Rakhine State riots, a series of conflicts that primarily involved the ethnic Rakhine Buddhist people and the Rohingya Muslim people in the northern Rakhine State—an estimated 90,000 people were displaced as a result of the riots. The Burmese government previously identified the Rohingya as a group of illegal migrants; however, the ethnic group has lived in Burma for numerous centuries.
In 2007 the German professor Bassam Tibi suggested that the Rohingya conflict may be driven by an Islamist political agenda to impose religious laws, while non-religious causes have also been raised, such as a lingering resentment over the violence that occurred during the Japanese occupation of Burma in World War II—during this time period the British allied themselves with the Rohingya and fought against the puppet government of Burma (comprised mostly of Bamar Japanese) that helped to establish the Tatmadaw military organization that remains in power as of March 2013.
A UN envoy reported in March 2013 that unrest had re-emerged between Burma's Buddhist and Muslim communities, with violence spreading to towns that are located closer to Yangon. The BBC News media outlet obtained video footage of a man with severe burns who received no assistance from passers-by or police officers even though he was lying on the ground in a public area. The footage was filmed by members of the Burmese police force in the town of Meiktila and was used as evidence that Buddhists continued to kill Muslims after the European Union sanctions were lifted on 23 April 2013.
Government and politics
The constitution of Burma, its third since independence, was drafted by its military rulers and published in September 2008. The country is governed as a presidential republic with a bicameral legislature, with a portion of legislatures appointed by the military and others elected in general elections. The current head of state, inaugurated as President on 30 March 2011, is Thein Sein.
The legislature, called the Pyidaungsu Hluttaw, is bicameral and made up of two houses: The 224-seat upper house Amyotha Hluttaw (House of Nationalities) and the 440-seat lower house Pyithu Hluttaw (House of Representatives). The upper house consists of 224 member of which 168 are directly elected and 56 are appointed by the Burmese Armed Forces while the lower house consists of 440 members of which 330 are directly elected and 110 are appointed by the armed forces. The major political parties are the National League for Democracy, National Democratic Force and the two backed by the military: the National Unity Party, and the Union Solidarity and Development Party.
Burma's army-drafted constitution was approved in a referendum in May 2008. The results, 92.4% of the 22 million voters with an official turnout of 99%, are considered suspect by many international observers and by the National league of democracy with reports of widespread fraud, ballot stuffing, and voter intimidation.
The elections of 2010 resulted in a victory for the military-backed Union Solidarity and Development Party and various foreign observers questioned the fairness of the elections. One criticism of the election was that only government sanctioned political parties were allowed to contest in it and the popular National League for Democracy was declared illegal and is still barred from political activities. However, immediately following the elections, the government ended the house arrest of the democracy advocate and leader of the National League for Democracy, Aung San Suu Kyi. and her ability to move freely around the country is considered an important test of the military's movement toward more openness. After unexpected reforms in 2011, NLD senior leaders have decided to register as a political party and to field candidates in future by-elections.
Burma rates as a highly corrupt nation on the Corruption Perceptions Index with a rank of 180th out of 183 countries worldwide and a rating of 1.5 out of 10 (10 being least corrupt and 0 being highly corrupt) as of 2011.
Foreign relations
Though the country's foreign relations, particularly with Western nations, have been strained, relations have thawed since the reforms following the 2010 elections. After years of diplomatic isolation and economic and military sanctions, the United States relaxed curbs on foreign aid to Burma in November 2011 and announced the resumption of diplomatic relations on 13 January 2012 The European Union has placed sanctions on Burma, including an arms embargo, cessation of trade preferences, and suspension of all aid with the exception of humanitarian aid. U.S. and European government sanctions against the former military government, coupled with boycotts and other direct pressure on corporations by supporters of the democracy movement, have resulted in the withdrawal from the country of most U.S. and many European companies. On 13 April 2012 British Prime Minister David Cameron called for the economic sanctions on Burma to be suspended in the wake of the pro-democracy party gaining 43 seats out of a possible 45 in the 2012 by-elections with the party leader, Aung San Suu Kyi becoming a member of the Burmese parliament.
Despite Western isolation, Asian corporations have generally remained willing to continue investing in the country and to initiate new investments, particularly in natural resource extraction. The country has close relations with neighbouring India and China with several Indian and Chinese companies operating in the country. Under India's Look East policy, fields of cooperation between India and Burma include remote sensing, oil and gas exploration, information technology, hydro power and construction of ports and buildings. In 2008, India suspended military aid to Burma over the issue of human rights abuses by the ruling junta, although it has preserved extensive commercial ties, which provide the regime with much-needed revenue. The thaw in relations began on 28 November 2011, when Belarusian Prime Minister Mikhail Myasnikovich and his wife Ludmila arrived in the capital, Naypyidaw, the same day as the country received a visit by US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who also met with pro-democracy opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi. International relations progress indicators continued in September 2012 when Aung San Suu Kyi visited to the US followed by Burma's reformist president visit to the United Nations.
In May 2013, Sein became the first Myanmar president to visit the U.S. White House in 47 years and President Barack Obama praised the former general for political and economic reforms, and the cessation of tensions between Myanmar and the U.S. Political activists objected to the visit due to concerns over human rights abuses in Myanmar but Obama assured Sein that Myanmar will receive the support from the U.S. Prior to President Sein, the last Myanmar leader to visit the White House was Ne Win in September 1966. The two leaders discussed Sein's intention to release more political prisoners, the institutionalization of political reform and rule of law, and ending ethnic conflict in Myanmar—the two governments agreed to sign a bilateral trade and investment framework agreement on May 21, 2013.
In June 2013, Myanmar will hold its first ever summit, the World Economic Forum on East Asia 2013. A regional spinoff of the annual World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, the summit will be held June 5–7 and will be attended by 1,200 participants, including 10 heads of state, 12 ministers and 40 senior directors from around the world.
Visits by Western leaders

In mid October, 2012. former UK Prime Minister Tony Blair "led a delegation" to shake hands with President Thein Sein, and met with lower house speaker Shwe Mann. A British embassy spokesperson said he was there on behalf of The Office of Tony Blair, an umbrella group of foundations—inter-faith, sports, etc.—and governance initiatives that he started up after leaving office. The spokesperson said only that he had "productive discussions about the reform process".
On 3 November 2012 European Commission President José Manuel Barroso met with Myanmar's President Thein Sein in Myanmar.
On 6 November 2012 Australia's Prime Minister, Julia Gillard met with Myanmar's President Thein Sein on the sidelines of the 9th Asia–Europe Meeting becoming the first Australian head of government to meet Burma's leader in nearly 30 years.
On 12 November 2012 Sweden's Prime Minister, Fredrik Reinfeldt, met President U Thein Sein at the presidential palace in the new capital, Naypyidaw, while being accompanied on his visit by the Swedish Trade Minister Ewa Björling and two business delegations.
On 19 November 2012, US President Barack Obama visited Burma following his 2012 reelection and was accompanied by Hillary Clinton, returning almost a year after her first visit. Though he did not visit the capital, President Obama delivered a speech at Rangoon University, out of respect for the university where opposition to colonial rule first took hold. Obama's speech was broadcast live via Burmese state television channels but its simultaneous spoken translations was stopped when Obama began speaking about the Kachin Conflict. Obama also stated that recent violence in Rakhine state during the 2012 Rakhine State riots had to be addressed, he called for an end to communal violence between Muslims and Buddhists and then left to visit Thailand.
Military relations
Burma has received extensive military aid from India and China in the past According to some estimates, Burma has received more than US$200 million in military aid from India. Burma has been a member of ASEAN since 1997. Though it gave up its turn to hold the ASEAN chair and host the ASEAN Summit in 2006, it is scheduled to chair the forum and host the summit in 2014. In November 2008, Burma's political situation with neighbouring Bangladesh became tense as they began searching for natural gas in a disputed block of the Bay of Bengal. The fate of Rohingya refugees also remains an issue between Bangladesh and Burma.
The country's armed forces are known as the Tatmadaw, which numbers 488,000. The Tatmadaw comprises the Army, the Navy, and the Air Force. The country ranked twelfth in the world for its number of active troops in service. The military is very influential in the country, with all top cabinet and ministry posts usually held by millitary officials. Official figures for military spending are not available. Estimates vary widely because of uncertain exchange rates, but Burma's military forces' expenses are high. The country imports most of its weapons from Russia, Ukraine, China and India.
The country is building a research nuclear reactor near Pyin Oo Lwin with help from Russia. It is one of the signatories of the nuclear non-proliferation pact since 1992 and a member of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) since 1957. The military junta had informed the IAEA in September 2000 of its intention to construct the reactor. The research reactor outbuilding frame was built by ELE steel industries limited of Yangon/Rangoon and water from Anisakhan/BE water fall will be used for the reactor cavity cooling system.
In 2010 as part of the Wikileaks leaked cables, Burma was suspected of using North Korean construction teams to build a fortified Surface-to-Air Missile facility.
Until 2005, the United Nations General Assembly annually adopted a detailed resolution about the situation in Burma by consensus. But in 2006 a divided United Nations General Assembly voted through a resolution that strongly called upon the government of Burma to end its systematic violations of human rights. In January 2007, Russia and China vetoed a draft resolution before the United Nations Security Council calling on the government of Burma to respect human rights and begin a democratic transition. South Africa also voted against the resolution.
On 19 November 2012, Barack Obama became the first American president to visit Myanmar.
Human rights
There is consensus that the military regime in Burma is one of the world's most repressive and abusive regimes. On 9 November 2012, Samantha Power, Barack Obama's Special Assistant to the President on Human Rights wrote on the White House blog in advance of the president's visit that "Serious human rights abuses against civilians in several regions continue, including against women and children." In addition, members of the United Nations and major international human rights organisations have issued repeated and consistent reports of widespread and systematic human rights violations in Burma. The United Nations General Assembly has repeatedly called on the Burmese Military Junta to respect human rights and in November 2009 the General Assembly adopted a resolution "strongly condemning the ongoing systematic violations of human rights and fundamental freedoms" and calling on the Burmese Military Regime "to take urgent measures to put an end to violations of international human rights and humanitarian law." International human rights organizations including Human Rights Watch, Amnesty International and the American Association for the Advancement of Science have repeatedly documented and condemned widespread human rights violations in Burma. The Freedom in the World 2011 report by Freedom House notes that "The military junta has ... suppressed nearly all basic rights; and committed human rights abuses with impunity. The country [has] more than 2,100 political prisoners included about 429 members of the NLD, the victors in the 1990 elections." They have claimed that there is no independent judiciary in Burma. As of April 2013, according to Assistance Association for Political Prisoners, there are currently 176 political prisoners in Burmese prisons.
Child soldiers
Child soldiers have and continue to play a major part in the Burmese Army as well as Burmese rebel movements. The Independent reported in June, 2012 that "Children are being sold as conscripts into the Burmese military for as little as $40 and a bag of rice or a can of petrol." The UN's Special Representative of the Secretary-General for Children and Armed Conflict, Radhika Coomaraswamy, who stepped down from her position a week later, met representatives of the Government of Myanmar on 5 July 2012 and stated that she hoped the government's signing of an action plan would "signal a transformation." In September 2012, the Myanmar Armed Forces released 42 child soldiers and the International Labour Organization met with representatives of the government as well as the Kachin Independence Army to secure the release of more child soldiers. According to Samantha Power, a U.S. delegation raised the issue of child soldiers with the government in October, 2012 however she did not comment on the government's progress towards reform in this area.
A Bangkok Post article on 23 December 2012 reported that the Myanmar Armed Forces continued to use child soldiers including during the army's large offensive against the KIA in December 2012. The newspaper reported that "Many of them were pulled off Yangon streets and elsewhere and given a minimum of training before being sent to the front line."
Child/forced/slave labour, systematic sexual violence and human trafficking
Forced labour, human trafficking, and child labour are common. The military is also notorious for rampant use of sexual violence as an instrument of control, including allegations of systematic rapes and taking of sex slaves by the military, a practice continuing as of 2012. In 2007 the international movement to defend women's human rights issues in Burma was said to be gaining speed.
Genocide allegations and crimes against Rohingya people
Evidence has been gathered suggesting that the Burmese regime has marked certain ethnic minorities such as the Karen, Karenni and Shan for extermination or 'Burmisation'. This, however, has received little attention from the international community since it has been more subtle and indirect than the mass killings in places like Rwanda.
The Rohingya have consistently faced human rights abuses by the Burmese regime, which has refused to acknowledge them as Burmese citizens (despite some of them having lived in Burma for some generations) and attempted to forcibly expel Rohingya and bring in non-Rohingyas to replace them. This policy has resulted in the expulsion of approximately half of the Rohingya population from Burma. An estimated 90,000 people have been displaced in the recent sectarian violence between Rohingya Muslims and Buddhists in Burma's western Rakhine State. As a result of this policy Rohingya people have been described as "among the world's least wanted" and "one of the world's most persecuted minorities." They have been denied Burmese citizenship since a 1982 citizenship law was enacted. Rohingya are not allowed to travel without official permission, are banned from owning land and are required to sign a commitment to have no more than two children. In 2012, a riot broke out between ethnic Rakhine Buddhists and Rohingya Muslims, which left 78 people dead, 87 injured, and thousands of homes destroyed. It also displaced more than 52,000 people. As of July 2012, the Myanmar Government did not include the Rohingya minority group—classified as stateless Bengali Muslims from Bangladesh since 1982—on the government's list of more than 130 ethnic races and therefore the government says that they have no claim to Myanmar citizenship.
2012 Rakhine State riots
The 2012 Rakhine State riots are a series of ongoing conflicts between Rohingya Muslims and ethnic Rakhine in northern Rakhine State, Myanmar. The riots came after weeks of sectarian disputes and have been condemned by most people on both sides of the conflict.
The immediate cause of the riots is unclear, with many commentators citing the killing of ten Burmese Muslims by ethnic Rakhine after the rape and murder of a Rakhine woman as the main cause. Whole villages have been "decimated". Over 300 houses and a number of public buildings have been razed. According to Tun Khin, the president of the Burmese Rohingya Organisation UK (BROUK), as of 28 June 2012, 650 Rohingyas have been killed, 1,200 are missing, and more than 80,000 have been displaced. According to the Myanmar authorities, the violence, between ethnic Rakhine Buddhists and Rohingya Muslims, left 78 people dead, 87 injured, and thousands of homes destroyed. It displaced more than 52,000 people.
The government has responded by imposing curfews and by deploying troops in the regions. On 10 June 2012, a state of emergency was declared in Rakhine, allowing military to participate in administration of the region. The Burmese army and police have been accused of targeting Rohingya Muslims through mass arrests and arbitrary violence. A number of monks' organizations that played vital role in Burma's struggle for democracy have taken measures to block any humanitarian assistance to the Rohingya community.
Freedom of speech
Restrictions on media censorship were significantly eased in August 2012 following demonstrations by hundreds of protesters who wore shirts demanding that the government "Stop Killing the Press." The most significant change has come in the form that media organizations will no longer have to submit their content to a censorship board before publication. However, as explained by one editorial in the exiled press The Irrawaddy, this new "freedom" has caused some Burmese journalists to simply see the new law as an attempt to create an environment of self-censorship as journalists "are required to follow 16 guidelines towards protecting the three national causes — non-disintegration of the Union, non-disintegration of national solidarity, perpetuation of sovereignty — and "journalistic ethics" to ensure their stories are accurate and do not jeopardize national security."
Praise for the 2011 government reforms
Since the transition to new government in August 2011, Burma's human rights record has been improving according to the Crisis Group. The Freedom in the World 2012 report notes improvement due to new reforms. Previously rated as a 7, the lowest rating, for civil liberties and political rights, the release of political prisoners and a loosening of restriction has given Burma a 6 for civil liberties in the most recent Freedom in the World. The government has assembled a National Human Rights Commission consisted of 15 members from various backgrounds. Several activists in exile including Thee Lay Thee Anyeint members have returned to Burma after President Thein Sein's offer to expatriates to return home to work for national development. In an address to the United Nations Security Council in 22 September 2011, Burma's Foreign Minister Wunna Maung Lwin confirmed the release of prisoners in near future. The government has also relaxed reporting laws, but these remain highly restrictive. In September 2011, several banned websites, including YouTube, Democratic Voice of Burma and Voice of America, have been unblocked. A 2011 report by the Hauser Centre for Nonprofit Organizations found that while constrained by donor restrictions on contact with the Myanmar government, international humanitarian non governmental organisations (NGOs) see opportunities for effective advocacy with government officials, especially at the local level. At the same time, international NGOs are mindful of the ethical quandary of how to work with the government without bolstering or appeasing it.
Economy
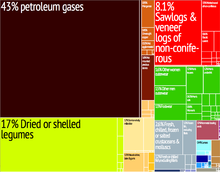
The country is one of the poorest nations in Southeast Asia, suffering from decades of stagnation, mismanagement and isolation. The lack of an educated workforce skilled in modern technology contributes to the growing problems of the economy. The country lacks adequate infrastructure. Goods travel primarily across the Thai border (where most illegal drugs are exported) and along the Irrawaddy River. Railways are old and rudimentary, with few repairs since their construction in the late 19th century. Highways are normally unpaved, except in the major cities. Energy shortages are common throughout the country including in Yangon and only 25% of the country's population has electricity.
The military government has the majority stakeholder position in all of the major industrial corporations of the country (from oil production and consumer goods to transportation and tourism).
The national currency is Kyat. Burma has a dual exchange rate system similar to Cuba. The market rate was around two hundred times below the government-set rate in 2006. Inflation averaged 30.1% between 2005 and 2007. Inflation is a serious problem for the economy.
-In 2010–2011, Bangladesh exported products worth $9.65 million to Myanmar against its import of $179 million. The annual import of medicine and medical equipment to Burma during the 2000s was 160 million USD.
In recent years, both China and India have attempted to strengthen ties with the government for economic benefit. Many nations, including the United States and Canada, and the European Union, have imposed investment and trade sanctions on Burma. The United States has banned all imports from Burma. Foreign investment comes primarily from China, Singapore, the Philippines, South Korea, India, and Thailand.
Background
Under British administration, Burma was the second-wealthiest country in South-East Asia. It had been the world's largest exporter of rice. Burma also had a wealth of natural and labour resources. It produced 75% of the world's teak and had a highly literate population. The country was believed to be on the fast track to development. However, agricultural production fell dramatically during the 1930s as international rice prices declined, and did not recover for several decades.
During World War II, the British destroyed the major oil wells and mines for tungsten, tin, lead and silver to keep them from the Japanese. Burma was bombed extensively by both sides. After a parliamentary government was formed in 1948, Prime Minister U Nu embarked upon a policy of nationalization and the state was declared the owner of all land. The government also tried to implement a poorly considered Eight-Year plan. By the 1950s, rice exports had fallen by two thirds and mineral exports by over 96% (as compared to the pre-World War II period). Plans were partly financed by printing money, which led to inflation. The 1962 coup d'état was followed by an economic scheme called the Burmese Way to Socialism, a plan to nationalise all industries, with the exception of agriculture. The catastrophic program turned Burma into one of the world's most impoverished countries. Burma's admittance to Least Developed Country status by the UN in 1987 highlighted its economic bankruptcy.
Agriculture
The major agricultural product is rice, which covers about 60% of the country's total cultivated land area. Rice accounts for 97% of total food grain production by weight. Through collaboration with the International Rice Research Institute 52 modern rice varieties were released in the country between 1966 and 1997, helping increase national rice production to 14 million tons in 1987 and to 19 million tons in 1996. By 1988, modern varieties were planted on half of the country's ricelands, including 98 percent of the irrigated areas. In 2008 rice production was estimated at 50 million tons.
Burma is also the world's second largest producer of opium, accounting for 8% of entire world production and is a major source of illegal drugs, including amphetamines. Opium bans implemented since 2002 after international pressure have left ex-poppy farmers without sustainable sources of income in the Kokang and Wa regions. They depend on casual labour for income.
Tourism
Since 1992, the government has encouraged tourism in the country. However, as of July 2006, fewer than 750,000 tourists entered the country annually. Burma's Minister of Hotels and Tourism Saw Lwin has stated that the government receives a significant percentage of the income of private sector tourism services. Much of the country is completely off-limits to tourists, and the military very tightly controls interactions between foreigners and the people of Burma, particularly the border regions. They are not to discuss politics with foreigners, under penalty of imprisonment, and in 2001, the Myanmar Tourism Promotion Board issued an order for local officials to protect tourists and limit "unnecessary contact" between foreigners and ordinary Burmese people.
Economic Sanctions
The Government of Burma had been under economic sanctions by the U.S. Treasury Department. There remains active debate as to the extent to which the American-led sanctions have had adverse effects on the civilian population or on the military rulers.
State Ownership/Corporatism and Economic liberalization post 2011
The military government has the majority stakeholder position in all of the major industrial corporations of the country (from oil production and consumer goods to transportation and tourism). In March 2012, a draft foreign investment law emerged, the first in more than 2 decades. Foreigners will no longer require a local partner to start a business in the country, and will be able to legally lease but not own property. The draft law also stipulates that Burmese citizens must constitute at least 25% of the firm's skilled workforce, and with subsequent training, up to 50-75%.
In 2012, the Asian Development Bank formally began re-engaging with the country, to finance infrastructure and development projects in the country. The United States, Japan and the European Union countries have also begun to reduce or eliminate economic sanctions to allow foreign direct investment which will provide the Burmese government with additional tax revenue.
Demographics
Burma has a population of about 56 million. Population figures are rough estimates because the last partial census, conducted by the Ministry of Home and Religious Affairs under the control of the military junta, was taken in 1983. No trustworthy nationwide census has been taken in Burma since 1931. There are over 600,000 registered migrant workers from Burma in Thailand, and millions more work illegally. Burmese migrant workers account for 80% of Thailand's migrant workers. Burma has a population density of 75 per square kilometre (190 /sq mi), one of the lowest in Southeast Asia. Refugee camps exist along Indian, Bangladeshi and Thai borders while several thousand are in Malaysia. Conservative estimates state that there are over 295,800 refugees from Burma, with the majority being Karenni, and Kayin and are principally located along the Thai-Burma border. There are nine permanent refugee camps along the Thai-Burma border, most of which were established in the mid-1980s. The refugee camps are under the care of the Thai-Burma Border Consortium (TBBC). Since 2006, over 55,000 Burmese refugees have been resettled in the United States.
There are over 53.42 million Buddhists, over 2.98 million Christians, over 2.27 million Muslims, over 300,000 Hindus and over 790,000 of those who believe in other religions in the country, according to an answer by Union Minister at Myanmar Parliament on 8 September 2011.
Ne Win's rise to power in 1962 and his relentless persecution of "resident aliens" (immigrant groups not recognised as citizens of the Union of Burma) led to an exodus/expulsion of some 300,000 Burmese Indians. They migrated to escape racial discrimination and wholesale nationalisation of private enterprise a few years later in 1964. The Anglo-Burmese at this time either fled the country or changed their names and blended in with the broader Burmese society.
Many Rohingya Muslims fled Burma and many refugees inundated neighbouring Bangladesh including 200,000 in 1978 as a result of the King Dragon operation in Arakan and 250,000 in 1991.
Largest cities
| Largest cities or towns of Myanmar http://www.geonames.org/MM/largest-cities-in-myanmar-%5Bburma%5D.html |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | City name | Division | Pop. | ||||||
 Yangon |
1 | Yangon | Yangon | 4,572,948 |  Naypyidaw |
||||
| 2 | Mandalay | Mandalay | 1,237,028 | ||||||
| 3 | Naypyidaw | Mandalay | 924,608 | ||||||
| 4 | Mawlamyaing | Mon | 451,011 | ||||||
| 5 | Bago | Bago | 248,899 | ||||||
| 6 | Pathein | Ayeyawady | 241,624 | ||||||
| 7 | Monywa | Sagaing | 185,783 | ||||||
| 8 | Meiktila | Mandalay | 181,744 | ||||||
| 9 | Sittwe | Rahkine | 181,172 | ||||||
| 10 | Mergui | Tanintharyi | 177,961 | ||||||
Ethnic groups
Burma is home to four major language families: Sino-Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, Austro-Asiatic, and Indo-European. Sino-Tibetan languages are most widely spoken. They include Burmese, Karen, Kachin, Chin, and Chinese. The primary Tai–Kadai language is Shan. Mon, Palaung, and Wa are the major Austroasiatic languages spoken in Burma. The two major Indo-European languages are Pali, the liturgical language of Theravada Buddhism, and English.
According to the UNESCO Institute of Statistics, Burma's official literacy rate as of 2000 was 89.9%. Historically, Burma has had high literacy rates. To qualify for least developed country status by the UN in order to receive debt relief, Burma lowered its official literacy rate from 78.6% to 18.7% in 1987.
Burma is ethnically diverse. The government recognises 135 distinct ethnic groups. While it is extremely difficult to verify this statement, there are at least 108 different ethnolinguistic groups in Burma, consisting mainly of distinct Tibeto-Burman peoples, but with sizeable populations of Tai–Kadai, Hmong–Mien, and Austroasiatic (Mon–Khmer) peoples. The Bamar form an estimated 68% of the population. 10% of the population are Shan. The Kayin make up 7% of the population. The Rakhine people constitute 4% of the population. Overseas Chinese form approximately 3% of the population. Burma's ethnic minority groups prefer the term "ethnic nationality" over "ethnic minority" as the term "minority" furthers their sense of insecurity in the face of what is often described as "Burmanisation"—the proliferation and domination of the dominant Bamar culture over minority cultures.
Mon, who form 2% of the population, are ethno-linguistically related to the Khmer. Overseas Indians comprise 2%. The remainder are Kachin, Chin, Anglo-Indians, Gurkha, Nepali and other ethnic minorities. Included in this group are the Anglo-Burmese. Once forming a large and influential community, the Anglo-Burmese left the country in steady streams from 1958 onwards, principally to Australia and the U.K.. Today, it is estimated that only 52,000 Anglo-Burmese remain in the country. There are 110,000 Burmese refugees in Thai border camps.
89% of the country's population are Buddhist, according to a report on ABC World News Tonight in May 2008 and the Buddha Dharma Education Association.
Language
Burmese, the mother tongue of the Bamar and official language of Burma, is related to Tibetan and to the Chinese languages. It is written in a script consisting of circular and semi-circular letters, which were adapted from the Mon script, which in turn was developed from a southern Indian script in the 8th century. The earliest known inscriptions in the Burmese script date from the 11th century. It is also used to write Pali, the sacred language of Theravada Buddhism, as well as several ethnic minority languages, including Shan, several Karen dialects, and Kayah (Karenni), with the addition of specialised characters and diacritics for each language. The Burmese language incorporates widespread usage of honorifics and is age-oriented. Burmese society has traditionally stressed the importance of education. In villages, secular schooling often takes place in monasteries. Secondary and tertiary education take place at government schools.
Religion
Many religions are practised in Burma. Religious edifices and orders have been in existence for many years. Festivals can be held on a grand scale. The Christian and Muslim populations do, however, face religious persecution and it is hard, if not impossible, for non-Buddhists to join the army or get government jobs, the main route to success in the country. Such persecution and targeting of civilians is particularly notable in Eastern Burma, where over 3000 villages have been destroyed in the past ten years. More than 200,000 Rohingya Muslims have settled in Bangladesh, to escape persecution, over the past 20 years.
89% of the population embraces Buddhism (mostly Theravāda). Other religions are practiced largely without obstruction, with the notable exception of some ethnic minorities such as the Muslim Rohingya people, who have continued to have their citizenship status denied and treated as illegal immigrants instead, and Christians in Chin State. 4% of the population practices Islam; 4% Christianity; 1% traditional animistic beliefs; and 2% follow other religions, including Mahayana Buddhism, Hinduism, East Asian religions and the Bahá'í Faith. However, according to a U.S. State Department's 2010 international religious freedom report, official statistics are alleged to underestimate the non-Buddhist population. Independent researchers put the Muslim population at 6 to 10% of the population. A tiny Jewish community in Rangoon had a synagogue but no resident rabbi to conduct services.
Although Hinduism is presently only practiced by 1% of the population, it was a major religion in Burma's past. Several strains of Hinduism existed alongside both Theravada Buddhism and Mahayana Buddhism in the Pyu period in the first millennium CE, and down to the Pagan period (9th to 13th centuries) when " Saivite and Vaishana elements enjoyed greater elite influence than they would later do."
Culture

A diverse range of indigenous cultures exist in Burma, the majority culture is primarily Buddhist and Bamar. Bamar culture has been influenced by the cultures of neighbouring countries. This is manifested in its language, cuisine, music, dance and theatre. The arts, particularly literature, have historically been influenced by the local form of Theravada Buddhism. Considered the national epic of Burma, the Yama Zatdaw, an adaptation of India's Ramayana, has been influenced greatly by Thai, Mon, and Indian versions of the play. Buddhism is practised along with nat worship, which involves elaborate rituals to propitiate one from a pantheon of 37 nats.
Mohinga, traditional Burmese rice noodles in fish soup, is widely considered to be Burma's national dish.
In a traditional village, the monastery is the centre of cultural life. Monks are venerated and supported by the lay people. A novitiation ceremony called shinbyu is the most important coming of age events for a boy, during which he enters the monastery for a short time. All male children in Buddhist families are encouraged to be a novice (beginner for Buddhism) before the age of twenty and to be a monk after the age of twenty. Girls have ear-piercing ceremonies (နားသ) at the same time. Burmese culture is most evident in villages where local festivals are held throughout the year, the most important being the pagoda festival. Many villages have a guardian nat, and superstition and taboos are commonplace.
British colonial rule introduced Western elements of culture to Burma. Burma's education system is modelled after that of the United Kingdom. Colonial architectural influences are most evident in major cities such as Yangon. Many ethnic minorities, particularly the Karen in the southeast and the Kachin and Chin who populate the north and northeast, practice Christianity. According to the The World Factbook, the Burman population is 68% and the ethnic groups comprise of 32%. However, the exiled leaders and organisations claims that ethnic population is 40%, which is implicitly contrasted with CIA report (official U.S. report).
Sport
The Lethwei, Bando, Banshay, Pongyi thaing martial arts and chinlone are the national sports in Burma.
Units of measure
According to The World Factbook, Burma is one of three countries along with Liberia and the United States of America that has not adopted the International System of Units (SI) metric system as their official system of weights and measures. The common units of measure are unique to Burma, but the government web pages use both imperial units. and metric units In June 2011, the Burmese government's Ministry of Commerce began discussing proposals to reform the measurement system and adopt the metric system used by most of its trading partners.
Geography
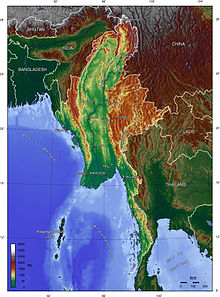
Burma, which has a total area of 678,500 square kilometres (262,000 sq mi), is the largest country in mainland Southeast Asia, and the 40th-largest in the world. It lies between latitudes 9° and 29°N, and longitudes 92° and 102°E. As of February 2011, Burma consisted of 14 states and regions, 67 districts, 330 townships, 64 sub-townships, 377 towns, 2914 Wards, 14220 village tracts and 68290 villages.
It is bordered on the northwest by the Chittagong Division of Bangladesh and the Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh states of India. Its north and northeast border straddles the Tibet Autonomous Region and Yunnan province for a Sino-Burman border total of 2,185 km (1,358 mi). It is bounded by Laos and Thailand to the southeast. Burma has 1,930 km (1,200 mi) of contiguous coastline along the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea to the southwest and the south, which forms one quarter of its total perimeter.
In the north, the Hengduan Mountains form the border with China. Hkakabo Razi, located in Kachin State, at an elevation of 5,881 metres (19,295 ft), is the highest point in Burma. Many mountain ranges, such as the Rakhine Yoma, the Bago Yoma, the Shan Hills and the Tenasserim Hills exist within Burma, all of which run north-to-south from the Himalayas. The mountain chains divide Burma's three river systems, which are the Irrawaddy, Salween (Thanlwin), and the Sittaung rivers. The Irrawaddy River, Burma's longest river, nearly 2,170 kilometres (1,348 mi) long, flows into the Gulf of Martaban. Fertile plains exist in the valleys between the mountain chains. The majority of Burma's population lives in the Irrawaddy valley, which is situated between the Rakhine Yoma and the Shan Plateau.
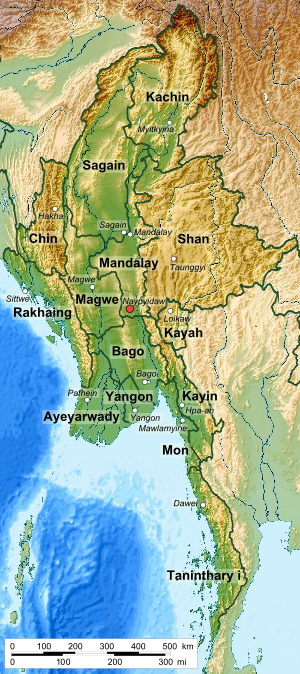
Administrative divisions (regions and states)
The country is divided into seven states (ပြည်နယ်) and seven regions (တိုင်းဒေသကြီး), formerly called divisions. The announcement on the renaming of division to regions was made on 20 August 2010. Regions are predominantly Bamar (that is, mainly inhabited by the dominant ethnic group). States, in essence, are regions that are home to particular ethnic minorities. The administrative divisions are further subdivided into districts, which are further subdivided into townships, wards, and villages.
Below are the number of districts, townships, cities/towns, wards, village Groups and villages in each divisions and states of Burma as of 31 December 2001:
| No. | State/Region | Districts | Town ships |
Cities/ Towns |
Wards | Village groups |
Villages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kachin State | 3 | 18 | 20 | 116 | 606 | 2630 |
| 2 | Kayah State | 2 | 7 | 7 | 29 | 79 | 624 |
| 3 | Kayin State | 3 | 7 | 10 | 46 | 376 | 2092 |
| 4 | Chin State | 2 | 9 | 9 | 29 | 475 | 1355 |
| 5 | Sagaing Region | 8 | 37 | 37 | 171 | 1769 | 6095 |
| 6 | Tanintharyi Region | 3 | 10 | 10 | 63 | 265 | 1255 |
| 7 | Bago Region | 4 | 28 | 33 | 246 | 1424 | 6498 |
| 8 | Magway Region | 5 | 25 | 26 | 160 | 1543 | 4774 |
| 9 | Mandalay Region | 7 | 31 | 29 | 259 | 1611 | 5472 |
| 10 | Mon State | 2 | 10 | 11 | 69 | 381 | 1199 |
| 11 | Rakhine State | 4 | 17 | 17 | 120 | 1041 | 3871 |
| 12 | Yangon Region | 4 | 45 | 20 | 685 | 634 | 2119 |
| 13 | Shan State | 11 | 54 | 54 | 336 | 1626 | 15513 |
| 14 | Ayeyarwady Region | 6 | 26 | 29 | 219 | 1912 | 11651 |
| Total | 63 | 324 | 312 | 2548 | 13742 | 65148 |
Climate
Much of the country lies between the Tropic of Cancer and the Equator. It lies in the monsoon region of Asia, with its coastal regions receiving over 5,000 mm (196.9 in) of rain annually. Annual rainfall in the delta region is approximately 2,500 mm (98.4 in), while average annual rainfall in the Dry Zone, which is located in central Burma, is less than 1,000 mm (39.4 in). Northern regions of the country are the coolest, with average temperatures of 21 °C (70 °F). Coastal and delta regions have an average maximum temperature of 32 °C (89.6 °F).
Wildlife
The country's slow economic growth has contributed to the preservation of much of its environment and ecosystems. Forests, including dense tropical growth and valuable teak in lower Burma, cover over 49% of the country, including areas of acacia, bamboo, ironwood and michelia champaca. Coconut and betel palm and rubber have been introduced. In the highlands of the north, oak, pine and various rhododendrons cover much of the land. Heavy logging since the new 1995 forestry law went into effect has seriously reduced forest acreage and wildlife habitat. The lands along the coast support all varieties of tropical fruits and once had large areas of mangroves although much of the protective mangroves have disappeared. In much of central Burma (the Dry Zone), vegetation is sparse and stunted.
Typical jungle animals, particularly tigers and leopards, occur sparsely in Burma. In upper Burma, there are rhinoceros, wild buffalo, wild boars, deer, antelope, and elephants, which are also tamed or bred in captivity for use as work animals, particularly in the lumber industry. Smaller mammals are also numerous, ranging from gibbons and monkeys to flying foxes and tapirs. The abundance of birds is notable with over 800 species, including parrots, peafowl, pheasants, crows, herons, and paddybirds. Among reptile species there are crocodiles, geckos, cobras, Burmese pythons, and turtles. Hundreds of species of freshwater fish are wide-ranging, plentiful and are very important food sources. For a list of protected areas, see List of protected areas of Burma.
Health
The general state of health care in Myanmar (Burma) is poor. The government spends anywhere from 0.5% to 3% of the country's GDP on health care, consistently ranking among the lowest in the world. Although health care is nominally free, in reality, patients have to pay for medicine and treatment, even in public clinics and hospitals. Public hospitals lack many of the basic facilities and equipment.
HIV/AIDS, recognised as a disease of concern by the Burmese Ministry of Health, is most prevalent among sex workers and intravenous drug users. In 2005, the estimated adult HIV prevalence rate in Burma was 1.3% (200,000–570,000 people), according to UNAIDS, and early indicators of any progress against the HIV epidemic are inconsistent. However, the National AIDS Programme Burma found that 32% of sex workers and 43% of intravenous drug users in Burma have HIV.
Burma's government spends the least percentage of its GDP on health care of any country in the world, and international donor organisations give less to Burma, per capita, than any other country except India. According to the report named "Preventable Fate", published by Doctors without Borders, 25,000 Burmese AIDS patients died in 2007, deaths that could largely have been prevented by antiretroviral therapy drugs and proper treatment.
In June 2011, the United Nations Population Fund released a report on The State of the World's Midwifery. It contained new data on the midwifery workforce and policies relating to newborn and maternal mortality for 58 countries. The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Myanmar is 240. This is compared with 219.3 in 2008 and 662 in 1990. The under 5 mortality rate, per 1,000 births is 73 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality is 47.
Education
The educational system of Burma is operated by the government agency, the Ministry of Education. Universities and professional institutes from upper Burma and lower Burma are run by two separate entities, the Department of Higher Education of Upper Burma and the Department of Higher Education of Lower Burma. Headquarters are based in Yangon and Mandalay respectively. The education system is based on the United Kingdom's system, due to nearly a century of British and Christian presences in Burma. Nearly all schools are government-operated, but there has been a recent increase in privately funded English language schools. Schooling is compulsory until the end of elementary school, probably about 9 years old, while the compulsory schooling age is 15 or 16 at international level.
There are 101 universities, 12 institutes, 9 degree colleges and 24 colleges in Burma, a total of 146 higher education institutions.
There are 10 Technical Training Schools, 23 nursing training schools, 1 sport academy and 20 midwifery schools.
There are 2047 Basic Education High Schools, 2605 Basic Education Middle Schools, 29944 Basic Education Primary Schools and 5952 Post Primary Schools. 1692 multimedia classrooms exist within this system.
There are four international schools acknowledged by WASC and College Board— The International School Yangon (ISY), Crane International School Yangon (CISM), Yangon International School (YIS) and International School of Myanmar (ISM) in Yangon.
Internet
In Burma, Internet access for the public is less than 1%, through Internet cafes. The activities of these institutions is highly regulated. There is censorship, and the authorities take the opportunity to view e-mail and posts in the Internet blogs. At least two Myanmar blogger were sent to prison. One of them, known under the name of Zarganar, was sentenced to 59 years of prison for publishing a video of destruction caused by the "Nargis" Cyclone in 2008, but have been released in October 12, 2011.


![Location of Burma (green)in ASEAN (dark grey) — [Legend]](../../images/933/93334.png)