
File:Cauchy sequence illustration2.png
- File
- File usage
- Learn more about Schools Wikipedia
Size of this preview: 640 × 410 pixels.
| |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
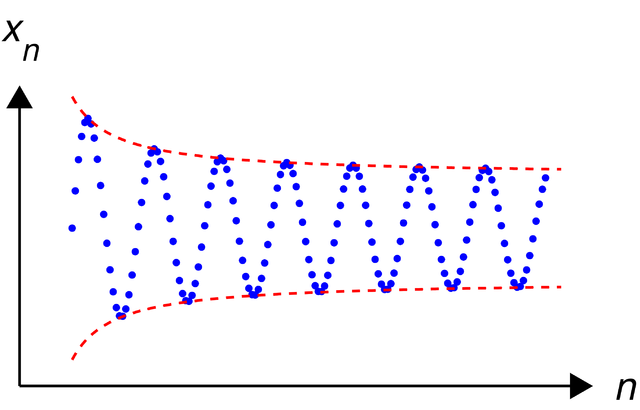
| Description | Illustration of en:Cauchy sequence |
| Date | 20:58, 3 June 2007 (UTC) |
| Source | self-made, with en:matlab |
| Author | Oleg Alexandrov |
| Permission ( Reusing this file) |
Public domain |
|
|
This chart was created with MATLAB. |
 |
File:Cauchy sequence illustration2.svg is a vector version of this file. It should be used in place of this raster image when superior. File:Cauchy sequence illustration2.png
For more information about vector graphics, read about Commons transition to SVG.
|
 |
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
 |
I, the copyright holder of this work, release this work into the public domain. This applies worldwide. In some countries this may not be legally possible; if so: I grant anyone the right to use this work for any purpose, without any conditions, unless such conditions are required by law. Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
Source code ( MATLAB)
% draw an illustration of a sequence that is not Cauchy function main() % prepare the screen and define some parameters figure(1); clf; hold on; axis equal; axis off; fontsize=30; thick_line=3; thin_line=2; black=[0, 0, 0]; red=[1, 0, 0]; blue=[0, 0, 1]; arrowsize=0.5; arrow_type=1; arrow_angle=30; % (angle in degrees) circrad=0.07; % radius of ball showing up in places B=9; X=0:0.06:B; f=inline('(X+2)./(X+0.8)', 'X'); Y=sin(5*X).*f(X); for i=1:length(X) ball(X(i), Y(i), circrad, blue); end X=0:0.05:(B+0.3); Z=f(X); plot(X, Z, 'r--', 'linewidth', thin_line) plot(X, -Z, 'r--', 'linewidth', thin_line) % draw the coordinate axes shift=-3; Kx=1.1; Ky=1.3; L=max(Y); arrow([-1 shift], [Kx*B, shift], thin_line, arrowsize, arrow_angle, arrow_type, black) arrow([-1, shift], [-1, Ky*L], thin_line, arrowsize, arrow_angle, arrow_type, black) text(Kx*B+0.6, shift, '\it{n}', 'fontsize', fontsize, 'HorizontalAlignment', 'c') text(-1, Ky*L+0.8, '\it{x_n}', 'fontsize', fontsize, 'HorizontalAlignment', 'c') % save to disk saveas(gcf, 'Cauchy_sequence_illustration2.eps', 'psc2') % export to eps function ball(x, y, r, colour) Theta=0:0.1:2*pi; X=r*cos(Theta)+x; Y=r*sin(Theta)+y; H=fill(X, Y, colour); set(H, 'EdgeColor', 'none'); function arrow(start, stop, th, arrow_size, sharpness, arrow_type, colour) % Function arguments: % start, stop: start and end coordinates of arrow, vectors of size 2 % th: thickness of arrow stick % arrow_size: the size of the two sides of the angle in this picture -> % sharpness: angle between the arrow stick and arrow side, in degrees % arrow_type: 1 for filled arrow, otherwise the arrow will be just two segments % color: arrow colour, a vector of length three with values in [0, 1] % convert to complex numbers i=sqrt(-1); start=start(1)+i*start(2); stop=stop(1)+i*stop(2); rotate_angle=exp(i*pi*sharpness/180); % points making up the arrow tip (besides the "stop" point) point1 = stop - (arrow_size*rotate_angle)*(stop-start)/abs(stop-start); point2 = stop - (arrow_size/rotate_angle)*(stop-start)/abs(stop-start); if arrow_type==1 % filled arrow % plot the stick, but not till the end, looks bad t=0.5*arrow_size*cos(pi*sharpness/180)/abs(stop-start); stop1=t*start+(1-t)*stop; plot(real([start, stop1]), imag([start, stop1]), 'LineWidth', th, 'Colour', colour); % fill the arrow H=fill(real([stop, point1, point2]), imag([stop, point1, point2]), colour); set(H, 'EdgeColor', 'none') else % two-segment arrow plot(real([start, stop]), imag([start, stop]), 'LineWidth', th, 'Colour', colour); plot(real([stop, point1]), imag([stop, point1]), 'LineWidth', th, 'Colour', colour); plot(real([stop, point2]), imag([stop, point2]), 'LineWidth', th, 'Colour', colour); end
Learn more about Schools Wikipedia
SOS Childrens Villages has brought Wikipedia to the classroom. SOS Childrens Villages believes education is an important part of a child's life. That's why we ensure they receive nursery care as well as high-quality primary and secondary education. When they leave school, we support the children in our care as they progress to vocational training or higher education. You can help by sponsoring a child.
