Khan Academy on a Stick
Exponential and logarithmic functions
An look at exponential and logarithmic functions including many of their properties and graphs.
-
 Exponential Growth Functions
cc
Exponential Growth Functions
ccExponential Growth Functions
-
 Ex: Graphing exponential functions
cc
Ex: Graphing exponential functions
ccGraphing Exponential Functions
-
 Subtracting Rational Expressions
cc
Subtracting Rational Expressions
ccSubtracting Rational Expressions
-
 Word Problem Solving- Exponential Growth and Decay
cc
Word Problem Solving- Exponential Growth and Decay
ccWord Problem Solving- Exponential Growth and Decay
-
 Exponential Growth
cc
Exponential Growth
ccExponential growth involving bacteria (some calculus in part c).
Exponential growth and decay
From compound interest to population growth to half lives of radioactive materials, it all comes down to exponential growth and decay.
-
 Graphing Logarithmic Functions
cc
Graphing Logarithmic Functions
ccGraphing Logarithmic Functions
-
 Logarithmic Scale
cc
Logarithmic Scale
ccUnderstanding how logarithmic scale is different from linear scale and why it could be useful
-
 Vi and Sal Talk About the Mysteries of Benford's Law
cc
Vi and Sal Talk About the Mysteries of Benford's Law
ccVi Hart visits Khan Academy and talks about Benford's Law with Sal
-
 Benford's Law Explanation (Sequel to Mysteries of Benford's Law)
cc
Benford's Law Explanation (Sequel to Mysteries of Benford's Law)
ccVi and Sal talk through the intuition of Benford's law (part 2)
-
 Solving Logarithmic Equations
cc
Solving Logarithmic Equations
ccSolving Logarithmic Equations
-
 Solving Logarithmic Equations
cc
Solving Logarithmic Equations
ccSolving Logarithmic Equations
Logarithmic functions
This tutorial shows you what a logarithmic function is. It will then go on to show the many times in nature and science that these type of functions are useful to describe what is happening.
-
 Introduction to interest
cc
Introduction to interest
ccWhat interest is. Simple versus compound interest.
-
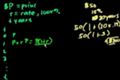 Interest (part 2)
cc
Interest (part 2)
ccMore on simple and compound interest
-
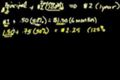 Introduction to compound interest and e
cc
Introduction to compound interest and e
ccCompounding interest multiple times a year.
-
 Compound Interest and e (part 2)
cc
Compound Interest and e (part 2)
ccCompounding 100% annual interest continuously over a year converges to e (2.71...)
-
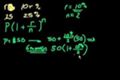 Compound Interest and e (part 3)
cc
Compound Interest and e (part 3)
ccContinuously compounding $P in principal at an annual interest rate of r for a year ends up with a final payment of $Pe^r
-
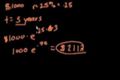 Compound Interest and e (part 4)
cc
Compound Interest and e (part 4)
ccContinuously compounding for multiple years.
Continuous compounding and e
This tutorial introduces us to one of the derivations (from finance and continuously compounding interest) of the irrational number 'e' which is roughly 2.71...