
True toad
Background to the schools Wikipedia
This Wikipedia selection is available offline from SOS Children for distribution in the developing world. SOS Children is the world's largest charity giving orphaned and abandoned children the chance of family life.
| True toads Temporal range: 57–0Ma Late Paleocene – Recent |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Common Toad or European Toad, Bufo bufo | |
| Territorial call of an Atelopus franciscus male | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Suborder: | Neobatrachia |
| Family: | Bufonidae Gray, 1825 |
| Genera | |
|
|
|
 |
|
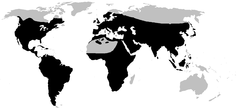
| Distribution of Bufonidae (in black) | |
Bufonidae is the family of the true toads, members of the order Anura (frogs and toads). They are the only family of anurans in which all members are known as "toads." The bufonids now comprise more than 35 genera, Bufo being the most widespread and well known.
Characteristics
True toads are widespread and occur natively on every continent except Australia and Antarctica, inhabiting a variety of environments, from arid areas to rainforest. Most lay eggs in paired strings that hatch into tadpoles, although, in the genus Nectophrynoides the eggs hatch directly into miniature toads.
True toads are toothless and generally warty in appearance. They have a pair of parotoid glands on the back of their heads. These glands contain an alkaloid poison which the toads excrete when stressed. The poison in the glands contains a number of toxins causing different effects. Bufotoxin is a general term. Different animals contain significantly different substances and proportions of substances. Some, like the cane toad Bufo marinus, are more toxic than others. Some " psychoactive toads," such as the Colorado River Toad Bufo alvaris, have been used recreationally for the effects of the bufotoxin.
Male toads possess a Bidder's organ. Under the right conditions, the organ becomes an active ovary and the toad, in effect, becomes female.
Taxonomy
Bufonidae contains about 500 species among 37 genera.
| Genus Latin Name and Author | Common Name | Species |
|---|---|---|
| Adenomus Cope, 1861 |
3
|
|
| Altiphrynoides Dubois, 1987 | Ethiopian Toads |
2
|
| Amietophrynus Frost et al., 2006 |
38
|
|
| Andinophryne Hoogmoed, 1985 | Andes Toads |
3
|
| Ansonia Stoliczka, 1870 | Stream Toads |
25
|
| Atelopus Duméril & Bibron, 1841 | Stubfoot Toads |
82
|
| Bufo Laurenti, 1768 | Toads |
150
|
| Bufoides Pillai & Yazdani, 1973 | Mawblang Toads |
1
|
| Capensibufo Grandison, 1980 | Cape Toads |
2
|
| Churamiti Channing & Stanley, 2002 |
1
|
|
| Crepidophryne Cope, 1889 | Cerro Utyum Toads |
3
|
| Dendrophryniscus Jiménez de la Espada, 1871 | Tree Toads |
7
|
| Didynamipus Andersson, 1903 | Four-digit Toads |
1
|
| Duttaphrynus Frost et al., 2006 |
6
|
|
| Epidalea Cope, 1864 | Natterjack Toads |
1
|
| Frostius Cannatella, 1986 | Frost's Toads |
2
|
| Ingerophrynus Frost et al., 2006 |
11
|
|
| Laurentophryne Tihen, 1960 | Parkers Tree Toads |
1
|
| Leptophryne Fitzinger, 1843 | Indonesia Tree Toads |
2
|
| Melanophryniscus Gallardo, 1961 | South American Redbelly Toads |
20
|
| Mertensophryne Tihen, 1960 | Snouted Frogs |
20
|
| Metaphryniscus Señaris, Ayarzagüena & Gorzula, 1994 |
1
|
|
| Nectophryne Buchholz & Peters, 1875 | African Tree Toads |
2
|
| Nectophrynoides Noble, 1926 | African Live-bearing Toads |
13
|
| Nimbaphrynoides Dubois, 1987 | Nimba Toads |
2
|
| Oreophrynella Boulenger, 1895 | Bush Toads |
8
|
| Osornophryne Ruiz-Carranza & Hernández-Camacho, 1976 | Plump Toads |
6
|
| Parapelophryne Fei, Ye & Jiang, 2003 |
1
|
|
| Pedostibes Günther, 1876 | Asian Tree Toads |
6
|
| Pelophryne Barbour, 1938 | Flathead Toads |
9
|
| Pseudepidalea Frost, et. al. 2006 |
16
|
|
| Pseudobufo Tschudi, 1838 | False Toads |
1
|
| Rhinella Fitzinger, 1826 | Beaked Toads |
72
|
| Schismaderma Smith, 1849 | African Split-skin Toads |
1
|
| Truebella Graybeal & Cannatella, 1995 |
2
|
|
| Werneria Poche, 1903 | Smalltongue Toads |
6
|
| Wolterstorffina Mertens, 1939 | Wolterstorff Toads |
3
|
