Khan Academy on a Stick
States of matter
-
 States of Matter
cc
States of Matter
ccIntroduction to the states or phases of matter.
-
 States of Matter Follow-Up
cc
States of Matter Follow-Up
ccMore on Plasma and Hydrogen bonds.
-
 Specific Heat, Heat of Fusion and Vaporization
cc
Specific Heat, Heat of Fusion and Vaporization
ccSpecifict heat and phase changes: Calculating how much heat is needed to convert 200g of ice at -10C to 110 degree steam.
-
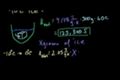 Chilling Water Problem
cc
Chilling Water Problem
ccHow much ice at -10 degrees C is necessary to get 500g of water down to 0 degrees C?
-
 Phase Diagrams
cc
Phase Diagrams
ccUnderstanding and interpreting phase diagrams
-
 Van Der Waals Forces
cc
Van Der Waals Forces
ccVan Der Waals Forces: London Dispersion Forces, Dipole Attractions, and Hydrogen Bonds.
-
 Covalent Networks, Metallic, and Ionic Crystals
cc
Covalent Networks, Metallic, and Ionic Crystals
ccCovalent Networks, Metallic, and Ionic Crystals: Some of the strongest molecular structures.
-
 Vapor Pressure
cc
Vapor Pressure
ccVapor Pressure, Volatility, and Evaporation
-
 Suspensions, Colloids and Solutions
cc
Suspensions, Colloids and Solutions
ccSuspensions, Colloids and Solutions. The difference between Molarity and Molality.
-
 Solubility
cc
Solubility
ccSolubility of salt and gas solutes in liquid solvent.
-
 Boiling Point Elevation and Freezing Point Suppression
cc
Boiling Point Elevation and Freezing Point Suppression
ccRaising or lowering the boiling or freezing point of a solution by adding solute.
-
 Change of State Example
cc
Change of State Example
ccSpecific Heat Capacity and Enthalpy of Vaporization example