Khan Academy on a Stick
Human biology
-
 The Lungs and Pulmonary System
cc
The Lungs and Pulmonary System
ccThe pulmonary system including the lungs, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and thoracic diaphragm
-
 Red blood cells
cc
Red blood cells
ccOxygen uptake by hemoglobin in red blood cells
-
 Circulatory System and the Heart
cc
Circulatory System and the Heart
ccIntroduction to the circulatory system and the heart
-
 Hemoglobin
cc
Hemoglobin
ccHemoglobin and its role in the circulatory system
-
 Anatomy of a Neuron
cc
Anatomy of a Neuron
ccIntroduction to the neuron and its anatomy
-
 Sodium Potassium Pump
cc
Sodium Potassium Pump
ccHow a sodium potassium pump can maintain a voltage gradient across a cell or neuron's membrane
-
 Correction to Sodium and Potassium Pump Video
cc
Correction to Sodium and Potassium Pump Video
ccCorrection to Sodium and Potassium Pump Video
-
 Electrotonic and Action Potentials
cc
Electrotonic and Action Potentials
ccHow electrotonic and action potentials propagate down cells
-
 Saltatory Conduction in Neurons
cc
Saltatory Conduction in Neurons
ccSaltatory conduction or how neurons use both electrotonic and action potentials to have signals move quickly while not losing strength.
-
 Neuronal Synapses (Chemical)
cc
Neuronal Synapses (Chemical)
ccHow one neuron can stimulate (or inhibit) another neuron at a chemical synapse
-
 Myosin and Actin
cc
Myosin and Actin
ccHow myosin and actin interact to produce mechanical force.
-
 Tropomyosin and troponin and their role in regulating muscle contraction
cc
Tropomyosin and troponin and their role in regulating muscle contraction
ccTropomyosin and troponin and their role in regulating muscle contraction. How calcium ion concentration dictates whether a muscle is contracting or not.
-
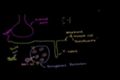 Role of the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum in Muscle Cells
cc
Role of the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum in Muscle Cells
ccThe role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in controlling calcium ion concentrations within the muscle cell
-
 Anatomy of a muscle cell
cc
Anatomy of a muscle cell
ccUnderstanding the structure of a muscle cell
-
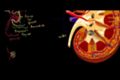 The Kidney and Nephron
cc
The Kidney and Nephron
ccOverview of how the nephrons in the kidney filter blood and reabsorb water and other molecules.
-
 Secondary Active Transport in the Nephron
cc
Secondary Active Transport in the Nephron
ccSecondary Active Transport in the Nephron